The Industrial Revolution T-Notes

MME Industrial Revolution

MME Industrial Revolution
Maglev Train Video
How it works
Vocabulary (Red) Facts (Yellow)
_____________________________________________________________
Industrial Revolution a period in the 18th and 19th century wheremachines began to do the work of human beings.
saw powered machinery, factories, and mass production
machines replaced humans and animals as tools
harsh conditions for millions of low-wage workers,
and great wealth for a privileged few.
I. Before the Industrial Revolution
cities were small, and most people lived in small towns
or farms
people produced most of their own clothing, food, furniture and tools
II. The Industrial Revolution is Born in England
many important raw materials as well as colonies
where it could get more
Mercantilism a system where a nation imports raw materials from its coloniesand then sells them back as finished goods at a profit.
Textiles fabrics and clothing, first main industry
textile mills used water power
mills required cheap labor
children were often used, no laws against children working, could pay less.
Steam Engine revolutionized industry
A. Transportation
Steamboat early 1800s, invented by American Robert Fulton
Steam Locomotive early 1800s, Richard Trevithick in England
John MacAdam road paving process, smoother roads
B. Communication
Telegraph England, 1837-allowed messages to be sent and received
quickly
Samuel Morse American simplified the telegraph and invented Morse Code
Trans-Atlantic Cable 1866, telegraph cable laid across bottom of Atlantic Ocean
C. Quality of Life
wages were low. Children used because were cheap
20% of all workers in Britain 1860s were under age 15
adults who worked in factories were paid low wages.
There were no laws for forty-hour week or
worker safety
no such thing as Workman's Comp.
Workers were packed into slum housing
pollution was terrible and disease was common in cities
The Breaker Boys
Triangle Shirtwaist Fire
I'm Just a Bill: Schoolhouse Rock

?Child Labor in the Industrial Revolution
Child Labor Bill Names of Group Members:
Primary Source Review
1. Go through the packet, reading every caption out loud with your small group and analyze the photographs.
2. Write a bill to change the law on Child Labor as if it were the year 1910.
3. Included the following in the bill
a. Your new proposed minimum age for hourly workers, and your reasoning for this new minimum age.
b. Your proposed wage for underage workers (if you allow it). Should it be the same, less or more than an adult worker?
c. Exceptions to the minimum age (children working on parents’ farm or business, paper carriers, etc)
d. Penalties for employers who violate the minimum age law.
4. Fill in the Bill template below for your bill.
5. Due Thursday for 1-3. Due Friday for 5.
Using the form below (or any similar template), fill in your ideas. (Lines are numbered for easy reference; when typing your bill, remember that, to avoid putting periods after each number, you can “customize” your list.)
1 (Title) A BILL TO . . .
2 Be it enacted by this Student Congress that (Write the main idea that you want to happen.)
Section 1: (If necessary, explain your idea further. You may need even more sections to outline the idea fully.)
Section 2: (Explain how the law will be enforced—who will do it, what will the penalties be? You might decide to use subsections to present these points in an outline form.)
Section 3: (State how the legislation will be funded if it will require a public expenditure—an additional tax, a surcharge on some product or service, a different allocation of current funds, etc.)
Section 4: (State directly when the legislation will take effect and what current law(s) will be superseded by the proposed law.)
Respectfully submitted,
Your name or school

Cartoon for the 8-hour day below.

The Industrial Revolution Part Two
T-Notes
Red (Vocab) Yellow (definitions/ideas)
there were few laws regulating what business could do in the early
part of the Industrial Revolution
Monopoly when a business has no competition, it can pretty much do what
it wants, including set prices.
American Monopoly Businesses bribed politicians and so they had control of state
and federal government at times in the late 1800s.
Laissez-Faire "Leave it alone" in French. Believed government should not
interfere in business.
Adam Smith English economist. Wrote Wealth of Nations. Explained ideas
of laissez-faire capitalism.
Capitalism a system where private individuals own the businesses and price
is determined by the law of supply and demand.
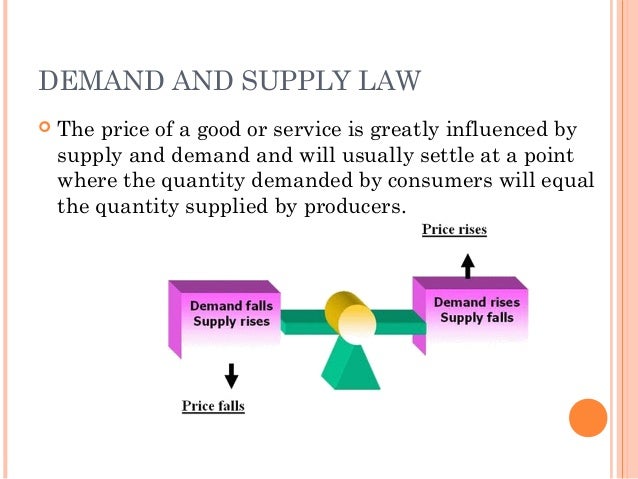
Law of Supply and Demand when demand greater than supply, price goes up
when demand less than supply, price goes down

reformers begin to wonder if the government should regulate business and employers/
employees
Progressives people who wanted to get corruption out of government and regulate
big business.
Muckrakers Progressives in journalism, writing and photography who pointed out
the corruption of government and the abuses of big business.
Upton Sinclair/The Jungle Writer who wrote about abuses in the Chicago meat-packing industry.
Read by many Americans, influenced President Roosevelt
Made President Theodore Roosevelt sick and convinced him govern-
ment regulation of big business was necessary.
Roosevelt passed progressive laws to protect consumers and workers.
Jaob Riis muckraker, writer and photographer. wrote the book "How the Other Half
Lives" about life in the slums.
Unions groups of workers who band together to get better wages and benefits
Business Owners hated unions and tried to destroy them
Rights Gained By Labor Unions weekends without work
breaks at work, including lunch
paid vacation
family and medical leave
sick leave
Social Security
Minimum Wage
Civil Rights Act
8-hour work day
Overtime Pay
Child Labor Law
Workplace Safety
40-hour-week
workman's comp
unemployment insurance
Reading 1: The Jungle Name
Morris 2018
Read the excerpt from Upton Sinclair’s The Jungle and then answer the questions below.
I. Easy Questions
1.
Why is it dangerous to scrape or cut your finger
in the pickling room?
2.
Judging
from the first paragraph, pickling fluid is similar to what fluid?
3.
What happened to the beef-boners and trimmers
thumbs, and why?
4.
Why would they have no fingernails?
5.
Why was it common for men in the steaming rooms
to catch tuberculosis?
6.
Describe the job of a beef-lugger.
7.
Why did woolpluckers loose their fingers?
8.
Why did many loose parts of their hands at the
stamping-machines?
9.
Why did hoisters walk with a permanent stoop?
10.
How was it possible for some workers to end up
being packaged as lard?
II. Idea Questions
1.
Why do you think conditions like this were
allowed to exist in 1900?
2.
Are there any types of food that you feel is
dangerous today and should be better regulated?
If so, what and why? If not, why
not?
3.
Are there any occupations today which could use
more regulation? If so, what are
they? If not, why don’t you think so?
4.
Should the government be able to ban sugared
soft drinks to curb obesity? Why or why
not?
5.
When does regulation become too intrusive in the
lives of people living in a nation or an area?
| Strikers face down the Army |
Study Guide Wednesday, May
10
Industrial Revolution
Study Guide Morris
1.
What was the
Industrial Revolution?
2.
Where did
it start and why did it start there?
3.
How did the
IR change the lives of the people who were alive at the time?
4.
How did it change
our lives today?
5.
The first
industry was _____________.
6.
7.
Why was the
telegraph so important?
8.
What was the
Trans-Atlantic Cable and why was it important?
9.
What happened to
the quality of life for many people during the industrial revolution?
10.
How did the use
of machines effect workers?
11.
Why were children often used as workers?
12.
Why could
factories and mines hire children?
13.
Why were there no
laws protecting workers?
14.
What was life
like in a big industrial city?
15.
What is a
tenement?
16.
What is a
monopoly?
17.
Many
believed in laissez-faire capitalism during the early part of the Industrial
Revolution? What is laissez-faire? What is capitalism?
18.
Explain the law
of supply and demand. If S (supply) is
greater than D (Demand), then P (price) does what? If S is greater than D, then price does
what? ? What is the ideal situation in a
capitalist economy? Define it.
19.
Why didn’t
government do more to help workers?
20.
Who was Adam
Smith and why is he important?
21.
Explain the law
of supply and demand and how prices move to equilibrium.
22.
Why did many
reformers and progressives feel laissez-faire capitalism might not be the best
way to run things?
23.
What is a
progressive?
24.
What is a
muckraker and why were muckrakers important?
25.
Who was Upton
Sinclair? What did he write? Why was this book so important?
26.
Who was Jacob
Riis? What did he do? Why is he important?
27.
Who was the first
real progressive President? What did he do?
28.
What is a labor
union and why were unions created? Give some goals of early labor unions.
29.
How did business
treat labor unions?
30.
What rights did
workers win from the labor movement?
31.
Why did the
industrial revolution lead to new ideas about economics and government, such as
socialism and communism?
32.
What happened at
the Triangle Shirtwaist Factory in 1911?
33.
Who was the first
progressive president of the United States?

Economic Systems T-Notes
There are four types of economic systems: traditional, Market, Command and Mixed.
Word Explanation
Economic System 1. a nation's resources are used to produce goods and services
2. goods and services are distributed to buyers
Functions of an Economy How much to produce?
What to produce?
How to produce?
For whom to produce
Adaptability
How goods and services
are produced and divided up
depends on : 1. government's role
2. How much freedom people have to decide
Capital money used to create a business.
1. Traditional examples include eskimoes, Native American tribes. trade instead of cash
2. Market elies on consumption (buying) choices of consumers.
government not involved in market economy
Businesses are privately owned
Goal is large profits
Consumers drive what is produced.
Price determined by law of supply and demand
Advantages of a Market Economy 1. market is free
2. government not involved
3. variety keeps prices low, quality high
4. profits can go to new innovation and technonology
Disadvantages of a Market Economy 1. Companies don't always make what's needed
2. Businesses can take advantage of workers and consumers
3. few rich and many poor
4. pollution

3. Command Economy government runs the economy and owns businesses
Advantages of Command Economy 1. government runs economy for all
2. government decides what to produce
3. eliminates extra competition
4. government decides wages
5. greater emphasis on making sure everyone has enough
Disadvantages of Command Economy 1. no freedom of choice
2. surpluses or shortages of goods
3. Lack of incentive for workers to work hard
4. government can make things people do not want (like bombs)
5. Black market
4.
Mixed Economy 1. economic system with both market economy and government control
2. Examples, USA, Canada, European nations, Japan
3. goal of private sector is to maximize profits and goal of
government is to maximize social welfare.
4. government provices goods and services that private sector unwilling or unable to produce.
Advantages of a mixed Economy 1. government protection of workers and citizens
2. cooperation
Disadvantages of MixedEconomy 1. too much government regulation can hurt free enterprise
2. some government industries may run even though they lose
money.
3. gap between rich and poor similar to market economy








No comments:
Post a Comment